18 Nov A/R and A/P Reconciliation on Cash Basis Statements
A/R and A/P Reconciliation on Cash Basis Statements
The first and easiest approach is to decide that the software is technically correct, and leave it as is. A review of the open invoices and unpaid bills with their account coding will usually confirm that this is correct.
The most efficient way to do this is to perform the following procedures:
- 1. Create a Balance Sheet and change the date as needed
- 2. Confirm the report basis is cash
- 3. Create an open invoice and/or unpaid bills report as of the report date and confirm there are not any transactions that have not been “linked.”
- 4. If Accounts Receivable or Accounts Payable still has a balance, double click on it. This will create a report for the activity for the period
- 5. Click on modify report and then filters
- 6. Change the date from the beginning of the file to the Balance Sheet date (i.e. include all historical transactions but not future transactions) and the paid status to open. This will provide a list of the transactions and related amounts that are coded to a Balance Sheet account and have not been reversed automatically. In addition, payments are considered to be “closed” transactions so if there are payments that have not been applied to an invoice, they may not appear on the report and would need to be subtracted to arrive at the cash basis balance. Double check the unpaid bills or open invoice report as of the report date to determine if this issue exists or not.
- 7. It may prove helpful to modify the report to include the item column (check it on the display tab). Usually the transactions are sales tax, inventory, customer deposit liabilities, etc.
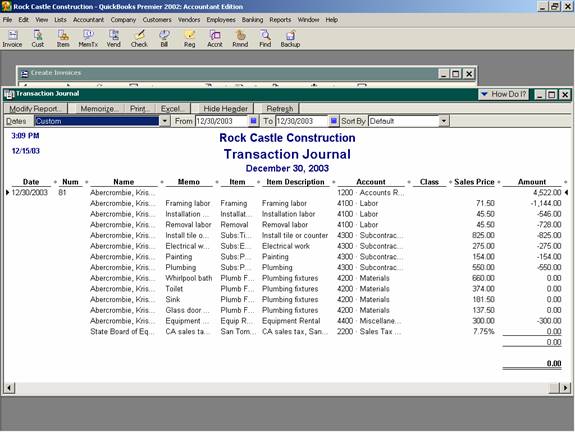
- 8. If the situation is not clear, it is possible to double click on the transaction to get to the form and then choose Reports > Transaction Journal to see the actual journal entry created by the form. This will display any additional accounts and amounts that are part of the entry for inventory items. Note: Any transactions that have been partially paid will be prorated to each line on the invoice so the amount on the report may not match the amount of the journal entry exactly. Note: It may be easier to analyze what is happening if the modify report button is used to add the debit and credit columns and eliminate the amount column on version 2002 and prior.
QBRA-2002: Open the form > Reports > Transaction Journal

Depending on the reporting basis of the financial statements and any related rules, it may be preferred to make a journal entry to reclassify the balance to a prepaid or accrued account, respectively. That is the second approach.
The second approach would be to make a journal entry to reclassify the balance. This approach works because journal entries are assumed to be on a cash basis as long as the A/R or A/P amount is not on the first line of the entry. The journal entry can only have one Accounts Receivable or Accounts Payable account and will need a customer or vendor for each Accounts Receivable or Accounts Payable transaction, respectively. Creating a Misc A/R customer or Misc A/P vendor will eliminate extraneous transactions in the history of any actual customers or vendors. The first day of the subsequent period, the journal entry should be reversed to eliminate the activity in Accounts Payable or Accounts Receivable. Keep in mind that the entry should typically be to a prepaid or accrued account, or to the actual Balance Sheet account that has been affected by the transaction based on the research performed in the first approach. An entry to income or cost of goods sold type accounts is incorrect. That is not the origination of the issue and doing so will distort both the Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss reports.
Final Notes
As you have learned, QuickBooks does permit switching between the cash and accrual methods of accounting for Accounts Receivable type accounts and Accounts Payable type accounts. If there are any other Balance Sheet accounts that should be eliminated, a journal entry will be required.

